Temperatur, CPU Auslastung Protokollieren
- Ersteller Hannibal7777
- Erstellt am
-
Ab sofort steht euch hier im Forum die neue Add-on Verwaltung zur Verfügung – eine zentrale Plattform für alles rund um Erweiterungen und Add-ons für den DSM.
Damit haben wir einen Ort, an dem Lösungen von Nutzern mit der Community geteilt werden können. Über die Team Funktion können Projekte auch gemeinsam gepflegt werden.
Was die Add-on Verwaltung kann und wie es funktioniert findet Ihr hier
Du verwendest einen veralteten Browser. Es ist möglich, dass diese oder andere Websites nicht korrekt angezeigt werden.
Du solltest ein Upgrade durchführen oder einen alternativen Browser verwenden.
Du solltest ein Upgrade durchführen oder einen alternativen Browser verwenden.
- Status
- Für weitere Antworten geschlossen.
Hallo Hannibal7777,
Bücher und Hardware zum Thema gibt es bei Amazon: Temperatur, CPU Auslastung Protokollieren
Bücher und Hardware zum Thema gibt es bei Amazon: Temperatur, CPU Auslastung Protokollieren
Matthieu
Benutzer
- Registriert
- 03. Nov. 2008
- Beiträge
- 13.222
- Reaktionspunkte
- 88
- Punkte
- 344
Zu Monitoring-Lösungen könnte ich hier auch Seiten schreiben. In Firmen kommt man um eine gewisse "Automatisierung" meist nicht drumherum. PRTG ist übrigens beim Server-Betrieb beliebter als beim Netzwerk-Team. Hat eben leicht unterschiedlichen Fokus. Erst recht wenn dann noch alles auf ITIL-Konformität abgeklopft hat (wenn die eigenen Prozesse nicht ITIL-konform sind, übersieht man das gern, aber externes muss immer genau passen).
Ich werfe mal noch eine ganz andere Richtung ins Boot. Ich bin derzeit mit NodeRed und ioBroker am Arbeiten, ggf. auch noch OpenHAB. Für ioBroker gibt es einen fertigen Synology-Adapter und die Visualisierung ist für privat unbegrenzt umsonst (und leicht umzusetzen)! Läuft bei mir in einer VM auf der 916+.
MfG Matthieu
Ich werfe mal noch eine ganz andere Richtung ins Boot. Ich bin derzeit mit NodeRed und ioBroker am Arbeiten, ggf. auch noch OpenHAB. Für ioBroker gibt es einen fertigen Synology-Adapter und die Visualisierung ist für privat unbegrenzt umsonst (und leicht umzusetzen)! Läuft bei mir in einer VM auf der 916+.
MfG Matthieu
- Registriert
- 05. März 2013
- Beiträge
- 2.584
- Reaktionspunkte
- 1.155
- Punkte
- 174
PRTG ist übrigens beim Server-Betrieb beliebter als beim Netzwerk-Team.
Das kann ich in unserem Falle nicht sagen, bei uns sind beide Truppen gleichermassen zufrieden mit PRTG...
TheTwist76
Benutzer
- Registriert
- 21. Apr. 2013
- Beiträge
- 227
- Reaktionspunkte
- 3
- Punkte
- 18
Hi,
gibt es hierzu vielleicht eine Anleitung wie man das aufsetzt? Würde mich sehr für diese Lösung interessieren.
Viele Grüße
Thorsten
Wie schon einmal an anderer Stelle hier erwähnt (finde ich gerade nicht wieder) kann man das ganz nett mit SNMP und Grafana/Influxdb in Docker lösen.
gibt es hierzu vielleicht eine Anleitung wie man das aufsetzt? Würde mich sehr für diese Lösung interessieren.
Viele Grüße
Thorsten
Anleitung ist übertrieben... aber so ging es bei mir:
Man setzt für Grafana, Influxdb und Telegraf je einen Standard Docker Container auf, die sich in einem eigenen Dockernetzwerk befinden sollten. Dann kennen sie sich auch gegenseitig am Namen.
Die Konfigurationsdateien und die InfluxDB Daten mounted man als Volume auf den Dockerhost. Jetzt nimmt man die Anleitung vom Dashboard und konfiguriert das SNMP wie beschrieben in die Telegraf Config herein und gibt als Output die Influxdb an. Den Grafana HTTP Port mappt man auf einen freien Port auf den Dockerhost. und startet alle Container. Am schnellsten geht das Aufsetzen mit einem Docker Compose File. Jetzt sollte man mit http://dockerhost:Port Grafana aufrufen können. In Grafana lädt man das Dashboard vom json file und gibt als Datenquelle die Influxdb an, die zu diesem Zeitpunkt schon Daten haben sollte. Das wars.
Man setzt für Grafana, Influxdb und Telegraf je einen Standard Docker Container auf, die sich in einem eigenen Dockernetzwerk befinden sollten. Dann kennen sie sich auch gegenseitig am Namen.
Die Konfigurationsdateien und die InfluxDB Daten mounted man als Volume auf den Dockerhost. Jetzt nimmt man die Anleitung vom Dashboard und konfiguriert das SNMP wie beschrieben in die Telegraf Config herein und gibt als Output die Influxdb an. Den Grafana HTTP Port mappt man auf einen freien Port auf den Dockerhost. und startet alle Container. Am schnellsten geht das Aufsetzen mit einem Docker Compose File. Jetzt sollte man mit http://dockerhost:Port Grafana aufrufen können. In Grafana lädt man das Dashboard vom json file und gibt als Datenquelle die Influxdb an, die zu diesem Zeitpunkt schon Daten haben sollte. Das wars.
BigRonin
Benutzer
- Registriert
- 08. Mai 2015
- Beiträge
- 1.156
- Reaktionspunkte
- 132
- Punkte
- 89
Sorry wenn ich hier so rein grätsche … wer nach einer einfachen Möglichkeit sucht ein paar DiskStation-Werte „auf / in der DS“ zu loggen und zu visualisieren, der könnte mit meinem Programm „AvrLogger“, eventuell das Richtige gefunden haben.
Zwar hat mein Programm erst vor kurzen den „Beta“-Status verlassen und es gibt noch vieles was ich integrieren und verbessern möchte, aber es funktioniert inzwischen recht zuverlässig.
Mein "AvrLogger" loggt, je nach Verfügbarkeit, bis zu 9 verschiedene Werte der DiskStation.
Dazu gehören:
- System Load
- CPU Temperatur
- Thermal-Status der DS
- Die Temperatur der wärmsten HDD
- Die Temperatur der kältesten HDD
- Den Mittelwert alles HDD Temperaturen
- Auf einigen DiskStations die Drehzahl der Lüfter in %
- Auf einigen DiskStations i2c-Temperatur-Werte
- UND einen externen „Umgebungs-Sensor“ per SNMP
Nahezu alles lässt sich per Konfig-Datei einstellen.
Leider habe ich noch keine ausführliche Beschreibung meines Programm-Packetes erstellt. Aber für die Script-Version. Das Programm „AvrLogger“ ist nahezu identisch mit der Script-Version.
Beide Varianten, Script und SPK, können von meinem Server herunter geladen werden:
Script
Beschreibung zur Script-Version
AvrLogger.SPK
Bitte die ReadMe’s lesen!
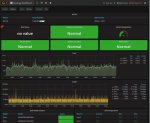
Stets aktueller Thermal-Staus meiner RS3617xs
Zwar hat mein Programm erst vor kurzen den „Beta“-Status verlassen und es gibt noch vieles was ich integrieren und verbessern möchte, aber es funktioniert inzwischen recht zuverlässig.
Mein "AvrLogger" loggt, je nach Verfügbarkeit, bis zu 9 verschiedene Werte der DiskStation.
Dazu gehören:
- System Load
- CPU Temperatur
- Thermal-Status der DS
- Die Temperatur der wärmsten HDD
- Die Temperatur der kältesten HDD
- Den Mittelwert alles HDD Temperaturen
- Auf einigen DiskStations die Drehzahl der Lüfter in %
- Auf einigen DiskStations i2c-Temperatur-Werte
- UND einen externen „Umgebungs-Sensor“ per SNMP
Nahezu alles lässt sich per Konfig-Datei einstellen.
Leider habe ich noch keine ausführliche Beschreibung meines Programm-Packetes erstellt. Aber für die Script-Version. Das Programm „AvrLogger“ ist nahezu identisch mit der Script-Version.
Beide Varianten, Script und SPK, können von meinem Server herunter geladen werden:
Script
Beschreibung zur Script-Version
AvrLogger.SPK
Bitte die ReadMe’s lesen!
Stets aktueller Thermal-Staus meiner RS3617xs
@Tommy2day
Ich habe das mal installiert.
Mir werden aber keine Daten angezeigt.
Wie kann ich denn das Dashboard mit den Daten der DS918+ füllen.
Wir werden keine Daten zur Auswahl wie Temp angeboten oder stehe ich auf dem Schlauch.
Könntest du mir bitte mal einen Tipp geben wie ich nun die Daten der Diskstation ins Dashboard bekomme?
Vielen Dank im Voraus.
Gruß
Jens
Ich habe das mal installiert.
Mir werden aber keine Daten angezeigt.
Wie kann ich denn das Dashboard mit den Daten der DS918+ füllen.
Wir werden keine Daten zur Auswahl wie Temp angeboten oder stehe ich auf dem Schlauch.
Könntest du mir bitte mal einen Tipp geben wie ich nun die Daten der Diskstation ins Dashboard bekomme?
Vielen Dank im Voraus.
Gruß
Jens
Hallo,
die Daten werden von Telegraf über snmp erfasst und an die Influxdb weitergegeben. Grafana liesst dann die Daten aus der Influxdb und zeigt sie an.
Zuerst ist natürlich snmp in der Diskstation zu aktivieren (Systemsteuerung->Terminal/SNMP->Tab SNMP). Der Einfachheit halber nehmen wir SNMPv1 und als Community public.
Jetzt setzen wir die Container auf. Den Telegraf-Container müssen wir noch etwas aufpeppen.
Als erstes die SNMP-MIBS von Synoloy downloaden und in ein unterverzeichnis mibs packen.
Dann bauen einen neuen Container für Telegraf. Dazu brauchen wir noch etwas Zusatzsoftware. Hierfür schreiben wir uns ein Dockerfile für Telegraf, was die MIBS lädt.
Jetzt noch ein Startscript
Die DNS-Parameter sind für die Namensauflösung da. Alternativ kann man mit --add-hostname die benötigten IPs für die DS und die Influxdb hinterlegen
Wir erstellen jetzt die Telegraf Konfiguration als config/telegraf.conf (hostname, influxdb-URL und Agents anpassen!)
Fortsetzung in Tel2
die Daten werden von Telegraf über snmp erfasst und an die Influxdb weitergegeben. Grafana liesst dann die Daten aus der Influxdb und zeigt sie an.
Zuerst ist natürlich snmp in der Diskstation zu aktivieren (Systemsteuerung->Terminal/SNMP->Tab SNMP). Der Einfachheit halber nehmen wir SNMPv1 und als Community public.
Jetzt setzen wir die Container auf. Den Telegraf-Container müssen wir noch etwas aufpeppen.
Als erstes die SNMP-MIBS von Synoloy downloaden und in ein unterverzeichnis mibs packen.
Dann bauen einen neuen Container für Telegraf. Dazu brauchen wir noch etwas Zusatzsoftware. Hierfür schreiben wir uns ein Dockerfile für Telegraf, was die MIBS lädt.
FROM telegraf:latest
#laden der bereitgestellten Synolgy MIBS
COPY mibs/* /usr/share/snmp/mibs/
#snmp-downloader von Debian zur Verarbeitung
RUN echo "deb http://http.us.debian.org/debian stable main contrib non-free" >/etc/apt/sources.list.d/nonfree.list && \
apt-get -y update && \
apt-get -y install snmp-mibs-downloader && \
apt clean
docker build --no-cache -t ${USER}/telegraf .
Jetzt noch ein Startscript
#!/bin/bash
CONFIG=$(pwd)/config
if [ ! -d $CONFIG ]; then
mkdir $CONFIG
fi
chmod -R a+rx $CONFIG
#run it
docker run -d --restart=always \
-v $CONFIG:/etc/telegraf:ro \
-v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock:ro \
-v /sys:/rootfs/sys:ro \
-v /proc:/rootfs/proc:ro \
-v /etc:/rootfs/etc:ro \
-v "${SHARED_DIR}/logs":/var/log/telegraf \
--dns "192.168.178.2" \
--dns-search "home.local" \
--env-file env_file \
--hostname $VMNAME \
--name ${VMNAME} \
${USER}/telegraf $@
Die DNS-Parameter sind für die Namensauflösung da. Alternativ kann man mit --add-hostname die benötigten IPs für die DS und die Influxdb hinterlegen
Wir erstellen jetzt die Telegraf Konfiguration als config/telegraf.conf (hostname, influxdb-URL und Agents anpassen!)
# Global tags can be specified here in key=value format.
[global_tags]
# dc = us-east-1 # will tag all metrics with dc=us-east-1
# rack = 1a
## Environment variables can be used as tags, and throughout the config file
# user = root
# Configuration for telegraf agent
[agent]
## Default data collection interval for all inputs
interval = "10s"
## Rounds collection interval to 'interval'
## ie, if interval="10s" then always collect on :00, :10, :20, etc.
round_interval = true
## Telegraf will send metrics to outputs in batches of at most
## metric_batch_size metrics.
## This controls the size of writes that Telegraf sends to output plugins.
metric_batch_size = 1000
## For failed writes, telegraf will cache metric_buffer_limit metrics for each
## output, and will flush this buffer on a successful write. Oldest metrics
## are dropped first when this buffer fills.
## This buffer only fills when writes fail to output plugin(s).
metric_buffer_limit = 10000
## Collection jitter is used to jitter the collection by a random amount.
## Each plugin will sleep for a random time within jitter before collecting.
## This can be used to avoid many plugins querying things like sysfs at the
## same time, which can have a measurable effect on the system.
collection_jitter = "0s"
## Default flushing interval for all outputs. You shouldn't set this below
## interval. Maximum flush_interval will be flush_interval + flush_jitter
flush_interval = "10s"
## Jitter the flush interval by a random amount. This is primarily to avoid
## large write spikes for users running a large number of telegraf instances.
## ie, a jitter of 5s and interval 10s means flushes will happen every 10-15s
flush_jitter = "0s"
## By default or when set to "0s", precision will be set to the same
## timestamp order as the collection interval, with the maximum being 1s.
## ie, when interval = "10s", precision will be "1s"
## when interval = "250ms", precision will be "1ms"
## Precision will NOT be used for service inputs. It is up to each individual
## service input to set the timestamp at the appropriate precision.
## Valid time units are "ns", "us" (or "µs"), "ms", "s".
precision = "s"
## Logging configuration:
## Run telegraf with debug log messages.
debug = false
## Run telegraf in quiet mode (error log messages only).
quiet = false
## Specify the log file name. The empty string means to log to stderr.
logfile = ""
## Override default hostname, if empty use os.Hostname()
hostname = "DS3018"
## If set to true, do no set the "host" tag in the telegraf agent.
omit_hostname = false
###############################################################################
# INPUT PLUGINS #
###############################################################################
# Read metrics about cpu usage
[[inputs.cpu]]
## Whether to report per-cpu stats or not
percpu = true
## Whether to report total system cpu stats or not
totalcpu = true
## If true, collect raw CPU time metrics.
collect_cpu_time = false
## If true, compute and report the sum of all non-idle CPU states.
report_active = false
# Read metrics about disk usage by mount point
[[inputs.disk]]
## By default stats will be gathered for all mount points.
## Set mount_points will restrict the stats to only the specified mount points.
# mount_points = ["/"]
## Ignore mount points by filesystem type.
ignore_fs = ["tmpfs", "devtmpfs", "devfs"]
# Read metrics about disk IO by device
[[inputs.diskio]]
## By default, telegraf will gather stats for all devices including
## disk partitions.
## Setting devices will restrict the stats to the specified devices.
# devices = ["sda", "sdb", "vd*"]
## Uncomment the following line if you need disk serial numbers.
# skip_serial_number = false
#
## On systems which support it, device metadata can be added in the form of
## tags.
## Currently only Linux is supported via udev properties. You can view
## available properties for a device by running:
## 'udevadm info -q property -n /dev/sda'
# device_tags = ["ID_FS_TYPE", "ID_FS_USAGE"]
#
## Using the same metadata source as device_tags, you can also customize the
## name of the device via templates.
## The 'name_templates' parameter is a list of templates to try and apply to
## the device. The template may contain variables in the form of '$PROPERTY' or
## '${PROPERTY}'. The first template which does not contain any variables not
## present for the device is used as the device name tag.
## The typical use case is for LVM volumes, to get the VG/LV name instead of
## the near-meaningless DM-0 name.
# name_templates = ["$ID_FS_LABEL","$DM_VG_NAME/$DM_LV_NAME"]
# Get kernel statistics from /proc/stat
[[inputs.kernel]]
# no configuration
# Read metrics about memory usage
[[inputs.mem]]
# no configuration
# Get the number of processes and group them by status
[[inputs.processes]]
# no configuration
# Read metrics about swap memory usage
[[inputs.swap]]
# no configuration
# Read metrics about system load & uptime
[[inputs.system]]
# no configuration
[[inputs.docker]]
## Docker Endpoint
## To use TCP, set endpoint = "tcp://[ip]:[port]"
## To use environment variables (ie, docker-machine), set endpoint = "ENV"
endpoint = "unix:///var/run/docker.sock"
## Only collect metrics for these containers, collect all if empty
container_names = []
## Timeout for docker list, info, and stats commands
timeout = "5s"
[[outputs.influxdb]]
## The full HTTP or UDP URL for your InfluxDB instance.
##
## Multiple URLs can be specified for a single cluster, only ONE of the
## urls will be written to each interval.
# urls = ["unix:///var/run/influxdb.sock"]
# urls = ["udp://127.0.0.1:8089"]
# urls = ["http://127.0.0.1:8086"]
urls = ["http://influxdb:8086"]
## The target database for metrics; will be created as needed.
# database = "telegraf"
###############################################################################
# INPUT PLUGINS #
###############################################################################
##
## Retrieves details via SNMP from remote agents
##
Fortsetzung in Tel2
Zuletzt bearbeitet:
Teil2:
Die Telegraf-config nun um die SNMP Konfiguration erweitern
(agents sind die abzufragenden DS)
Jetzt zuerst die Influxdb starten und dann den Telegraf Container mit dem Startscript.
Es sollte nun eine DB Telegraf in Influxdb erstellt werden und darin die gesammelten Metriken abgelegt werden. In grafana braucht man jetzt nur noch das Dashboard auf die Influxdb zeigen lassen und die Werte sollten langsam sichtbar werden.
HTH
Die Telegraf-config nun um die SNMP Konfiguration erweitern
(agents sind die abzufragenden DS)
##
## Synology
##
[[inputs.snmp]]
# List of agents to poll
agents = [ "ds3018","ds1812", "ds215j" ]
# Polling interval
interval = "60s"
# Timeout for each SNMP query.
timeout = "10s"
# Number of retries to attempt within timeout.
retries = 3
# SNMP version, UAP only supports v1
version = 2
# SNMP community string.
community = "public"
# The GETBULK max-repetitions parameter
max_repetitions = 30
# Measurement name
name = "snmp.SYNO"
##
## System Details
##
# System name (hostname)
[[inputs.snmp.field]]
is_tag = true
name = "sysName"
oid = "RFC1213-MIB::sysName.0"
# System vendor OID
[[inputs.snmp.field]]
name = "sysObjectID"
oid = "RFC1213-MIB::sysObjectID.0"
# System description
[[inputs.snmp.field]]
name = "sysDescr"
oid = "RFC1213-MIB::sysDescr.0"
# System contact
[[inputs.snmp.field]]
name = "sysContact"
oid = "RFC1213-MIB::sysContact.0"
# System location
[[inputs.snmp.field]]
name = "sysLocation"
oid = "RFC1213-MIB::sysLocation.0"
# System uptime
[[inputs.snmp.field]]
name = "sysUpTime"
oid = "RFC1213-MIB::sysUpTime.0"
# Inet interface
[[inputs.snmp.table]]
oid = "IF-MIB::ifTable"
[[inputs.snmp.table.field]]
is_tag = true
oid = "IF-MIB::ifDescr"
#Syno disk
[[inputs.snmp.table]]
oid = "SYNOLOGY-DISK-MIB::diskTable"
[[inputs.snmp.table.field]]
is_tag = true
oid = "SYNOLOGY-DISK-MIB::diskID"
#Syno raid
[[inputs.snmp.table]]
oid = "SYNOLOGY-RAID-MIB::raidTable"
[[inputs.snmp.table.field]]
is_tag = true
oid = "SYNOLOGY-RAID-MIB::raidName"
#Syno load
[[inputs.snmp.table]]
oid = "UCD-SNMP-MIB::laTable"
[[inputs.snmp.table.field]]
is_tag = true
oid = "UCD-SNMP-MIB::laNames"
# System memTotalSwap
[[inputs.snmp.field]]
name = "memTotalSwap"
oid = "UCD-SNMP-MIB::memTotalSwap.0"
# System memAvailSwap
[[inputs.snmp.field]]
name = "memAvailSwap"
oid = "UCD-SNMP-MIB::memAvailSwap.0"
# System memTotalReal
[[inputs.snmp.field]]
name = "memTotalReal"
oid = "UCD-SNMP-MIB::memTotalReal.0"
# System memAvailReal
[[inputs.snmp.field]]
name = "memAvailReal"
oid = "UCD-SNMP-MIB::memAvailReal.0"
# System memTotalFree
[[inputs.snmp.field]]
name = "memTotalFree"
oid = "UCD-SNMP-MIB::memTotalFree.0"
# System Status
[[inputs.snmp.field]]
name = "systemStatus"
oid = "SYNOLOGY-SYSTEM-MIB::systemStatus.0"
# System temperature
[[inputs.snmp.field]]
name = "temperature"
oid = "SYNOLOGY-SYSTEM-MIB::temperature.0"
# System powerStatus
[[inputs.snmp.field]]
name = "powerStatus"
oid = "SYNOLOGY-SYSTEM-MIB:owerStatus.0"
# System systemFanStatus
[[inputs.snmp.field]]
name = "systemFanStatus"
oid = "SYNOLOGY-SYSTEM-MIB::systemFanStatus.0"
# System cpuFanStatus
[[inputs.snmp.field]]
name = "cpuFanStatus"
oid = "SYNOLOGY-SYSTEM-MIB::cpuFanStatus.0"
# System modelName
[[inputs.snmp.field]]
name = "modelName"
oid = "SYNOLOGY-SYSTEM-MIB::modelName.0"
# System serialNumber
[[inputs.snmp.field]]
name = "serialNumber"
oid = "SYNOLOGY-SYSTEM-MIB::serialNumber.0"
# System version
[[inputs.snmp.field]]
name = "version"
oid = "SYNOLOGY-SYSTEM-MIB::version.0"
# System upgradeAvailable
[[inputs.snmp.field]]
name = "upgradeAvailable"
oid = "SYNOLOGY-SYSTEM-MIB::upgradeAvailable.0"
# System volume
[[inputs.snmp.table]]
oid = "HOST-RESOURCES-MIB::hrStorageTable"
[[inputs.snmp.table.field]]
is_tag = true
oid = "HOST-RESOURCES-MIB::hrStorageDescr"
# System ssCpuUser
[[inputs.snmp.field]]
name = "ssCpuUser"
oid = ".1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.11.9.0"
# System ssCpuSystem
[[inputs.snmp.field]]
name = "ssCpuSystem"
oid = ".1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.11.10.0"
# System ssCpuIdle
[[inputs.snmp.field]]
name = "ssCpuIdle"
oid = ".1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.11.11.0"
# Service users CIFS
[[inputs.snmp.table.field]]
name = "usersCIFS"
oid = "SYNOLOGY-SERVICES-MIB::serviceUsers"
oid_index_suffix = "1"
# Service users AFP
[[inputs.snmp.table.field]]
name = "usersAFP"
oid = "SYNOLOGY-SERVICES-MIB::serviceUsers"
oid_index_suffix = "2"
# Service users NFS
[[inputs.snmp.table.field]]
name = "usersNFS"
oid = "SYNOLOGY-SERVICES-MIB::serviceUsers"
oid_index_suffix = "3"
# Service users FTP
[[inputs.snmp.table.field]]
name = "usersFTP"
oid = "SYNOLOGY-SERVICES-MIB::serviceUsers"
oid_index_suffix = "4"
# Service users SFTP
[[inputs.snmp.table.field]]
name = "usersSFTP"
oid = "SYNOLOGY-SERVICES-MIB::serviceUsers"
oid_index_suffix = "5"
# Service users HTTP
[[inputs.snmp.table.field]]
name = "usersHTTP"
oid = "SYNOLOGY-SERVICES-MIB::serviceUsers"
oid_index_suffix = "6"
# Service users TELNET
[[inputs.snmp.table.field]]
name = "usersTELNET"
oid = "SYNOLOGY-SERVICES-MIB::serviceUsers"
oid_index_suffix = "7"
# Service users SSH
[[inputs.snmp.table.field]]
name = "usersSSH"
oid = "SYNOLOGY-SERVICES-MIB::serviceUsers"
oid_index_suffix = "8"
# Service users OTHER
[[inputs.snmp.table.field]]
name = "usersOTHER"
oid = "SYNOLOGY-SERVICES-MIB::serviceUsers"
oid_index_suffix = "9"
# UPS Status
[[inputs.snmp.table.field]]
name = "upsStatus"
oid = "SYNOLOGY-UPS-MIB::upsInfoStatus"
# UPS Load
[[inputs.snmp.table.field]]
name = "upsLoad"
oid = "SYNOLOGY-UPS-MIB::upsInfoLoadValue"
# UPS Battery Charge
[[inputs.snmp.table.field]]
name = "upsCharge"
oid = "SYNOLOGY-UPS-MIB::upsBatteryChargeValue"
# UPS Battery Charge Warning
[[inputs.snmp.table.field]]
name = "upsWarning"
oid = "SYNOLOGY-UPS-MIB::upsBatteryChargeWarning"
Jetzt zuerst die Influxdb starten und dann den Telegraf Container mit dem Startscript.
Es sollte nun eine DB Telegraf in Influxdb erstellt werden und darin die gesammelten Metriken abgelegt werden. In grafana braucht man jetzt nur noch das Dashboard auf die Influxdb zeigen lassen und die Werte sollten langsam sichtbar werden.
HTH
Dann bauen einen neuen Container für Telegraf. Dazu brauchen wir noch etwas Zusatzsoftware. Hierfür schreiben wir uns ein Dockerfile für Telegraf, was die MIBS lädt.
Wo mache ich das denn auf der Konsole der DS?
apt-get wird es doch auf der DS nicht geben?
Wo mache ich das denn auf der Konsole der DS?
apt-get wird es doch auf der DS nicht geben?
Nein, man braucht keine Zusatzsoftware, man braucht nur Docker. Das alles kann man auf der DS Konsole als Root machen.
Die Befehle im Dockerfile werden alle im Standard Telegraf-Container ausgeführt. Da gibt es dann apt-get.
Evtl. ist es hilfreich, sich zunächst über die Funktionsweise von Docker und Beziehungen von Containern einzulesen, sonst ist es vielleicht wirklich zu schwer zu verstehen.
Den Beitrag vom Februar mit docker-compose hattest Du ja schon gefunden.
Die Befehle im Dockerfile werden alle im Standard Telegraf-Container ausgeführt. Da gibt es dann apt-get.
Evtl. ist es hilfreich, sich zunächst über die Funktionsweise von Docker und Beziehungen von Containern einzulesen, sonst ist es vielleicht wirklich zu schwer zu verstehen.
Den Beitrag vom Februar mit docker-compose hattest Du ja schon gefunden.
Führe das Docker Build Kommando wie beschrieben aus, wenn Du das Dockerfile erstellt hast. Dann wird alles automatisch mit runtergeladen (das macht die Zeile FROM ....). Auch die anderen Schritte vom Dockerfile werden automatisch mit ausgeführt. Die DS braucht natürlich Internet-Zugriff. Statt -t ${User}/telegraf (das ist der neue Telegraf Imagename mit den Änderungen) kannst Du natürlich auch was anderes nehmen, musst das aber dann auch im run Script entsprechend anpassen
docker build --no-cache -t ${USER}/telegraf
"docker build" requires exactly 1 argument(s).
See 'docker build --help'.
Usage: docker build [OPTIONS] PATH | URL | -
Build an image from a Dockerfile
Bekomme mit dem Befehl eine Fehlermeldung.
"docker build" requires exactly 1 argument(s).
See 'docker build --help'.
Usage: docker build [OPTIONS] PATH | URL | -
Build an image from a Dockerfile
Bekomme mit dem Befehl eine Fehlermeldung.
Der Befehl heisst
Der Punkt am Ende hat seine Bedeutung. Er bezechnet das Arbeitsverzeichnis, wo das Dockerfile und alle anderen Files (wie das mibs Verzeichnis mit den Synology-MIBs) erwartet werdendocker build --no-cache -t ${USER}/telegraf .
Oh, OK nun habe ich das:
root@server:~# docker build --no-cache -t ${USER}/telegraf .
unable to prepare context: unable to evaluate symlinks in Dockerfile path: lstat /root/Dockerfile: no such file or directory
Muss ich die mibs vorher runterladen ? Wo bekomme ich die denn her.
Danke für deine Geduld....
root@server:~# docker build --no-cache -t ${USER}/telegraf .
unable to prepare context: unable to evaluate symlinks in Dockerfile path: lstat /root/Dockerfile: no such file or directory
Muss ich die mibs vorher runterladen ? Wo bekomme ich die denn her.
Danke für deine Geduld....
Hi,
ich habe die Datei in /root erstellt.
Dort habe ich auch nun den Ordner mibs mit den Dateien drin.
Ich bin in dem Ordner, aber ich bekomme die Fehlermeldung nicht weg.
Irgendein Ordner ist nicht da.
Hier meine telegraf Datei.
FROM telegraf:latest
COPY mibs/* /usr/share/snmp/mibs/
RUN echo "deb http://http.us.debian.org/debian stable main non-free" >/etc/apt/sources.list.d/nonfree.list && \
apt-get -y update && \
apt-get -y install snmp-mibs-downloader && \
apt clean
ich habe die Datei in /root erstellt.
Dort habe ich auch nun den Ordner mibs mit den Dateien drin.
Ich bin in dem Ordner, aber ich bekomme die Fehlermeldung nicht weg.
Irgendein Ordner ist nicht da.
Hier meine telegraf Datei.
FROM telegraf:latest
COPY mibs/* /usr/share/snmp/mibs/
RUN echo "deb http://http.us.debian.org/debian stable main non-free" >/etc/apt/sources.list.d/nonfree.list && \
apt-get -y update && \
apt-get -y install snmp-mibs-downloader && \
apt clean
Habe es mit:
root@server:~# docker build --no-cache -t telegraf:latest -f /root/telegraf . geschafft.
Habe nun einen neuen Container erstellt...!
Successfully built 2839fa275a26
Successfully tagged telegraf:latest
Nun muss ich noch wissen wo die Script gespeichert werden oder wo die hin müssen.
root@server:~# docker build --no-cache -t telegraf:latest -f /root/telegraf . geschafft.
Habe nun einen neuen Container erstellt...!
Successfully built 2839fa275a26
Successfully tagged telegraf:latest
Nun muss ich noch wissen wo die Script gespeichert werden oder wo die hin müssen.
- Status
- Für weitere Antworten geschlossen.
Kaffeautomat
Wenn du das Forum hilfreich findest oder uns unterstützen möchtest, dann gib uns doch einfach einen Kaffee aus.
Als Dankeschön schalten wir deinen Account werbefrei.